Agenda 2025 *
3 Days of Concentrated Connector Know-how
From Single Pair Ethernet, intelligent connectors, materials and coatings to additive manufacturing of connectors: this year's user congress program once again offers a wide range of topics.
On the first day, visitors can learn about the basics of connection technology in basic seminars** taking place in parallel.
On the second and third days, participants will receive in-depth, first-hand know-how in numerous presentations by experts from industry, science and research.
Monday, May 26, 2025 - Basic Seminars and EMC day
Registration of participants at the Vogel Convention Center (VCC)
Parallel Basic Seminars in the morning
(VCC seminar rooms)
Seminar 1: Connectors – important characteristics and terms
Dr.-Ing. Helmut Katzier | Engineering office for assembly and connection technology
What you will learn:
- Important characteristic values for connectors
- Technical explanation of the key figures
- Relevance of the parameters in different applications
Seminar 2: Basics of contact physics
Dr. Frank Ostendorf | TE Connectivity Germany GmbH
What you will learn:
- Basics of Electrical Connector Contacts
- Influence of coating and base materials
- Aging and failure mechanisms of connector contacts
Seminar 3: Copper materials for connectors
Stephan Gross | Boway Deutschland GmbH
What you will learn:
- Standard copper and copper materials
- Copper High-Performance Materials and Technical Properties & Surfaces
Seminar 4: Basics of cables and wires
Dr.-Ing. Philipp Baron | LAPP Holding SE
Maximilian Christians | LAPP Holding SE
What you will learn:
- Comprehensive overview of the structure and selection of cables and wires
- Future developments
Lunch break
Parallel Basic Seminars in the afternoon
(VCC seminar rooms)
Seminar 5: Use of Connectors
Herbert Endres | EndresConsult
What you will learn:
- Understanding of connector components, materials and properties
- Weighing up the compromises for the respective application
Seminar 6: Surface Coating of Contact Materials
Dr.-Ing. Stephanie Kißling | IMO Oberflächentechnik GmbH
What you will learn:
- Surface finish and geometric requirements of the base material
- Advantages and disadvantages of the coating metals used
- Differences between strip and single plating
Seminar 7: Selection of Plastics for Connectors
Martin Räthlein | Rosenberger GmbH & Co. KG
What you will learn:
- Requirements for plastics for connectors
- material properties of the various plastics
- Test methods for plastics
Seminar 8: Ensuring Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) in a Wired World
Dr. Heinz Zenkner | Publicly appointed and sworn expert for EMC
What you will learn:
- sources of high-frequency interference
- Measures along the transmission path to the interface
- Establishment of pre-compliance measurements for interference emissions from interfaces
Coffee break
Welcome to the EMC Day
Everything about Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) in Connection Technology

Kristin Rinortner
ELEKTRONIKPRAXIS
EMC and connectors: Which EMC rules must be observed when using and manufacturing connectors?

Engineering office for construction and connection technology
EMC game changer: Innovative cable designs for interference-free industrial plants

LAPP Holding SE
Coffee break
Poster-Slam
The speakers present their topics in short 5-minute presentations on the podium. The audience then awards the best presentation an award.
Ethernet Anywhere, how hybrid connector systems are changing automation

TE Connectivity Industrial GmbH
Description:
One Cable Automation, cabling sharing or hybrid technology - although these terms refer to fundamentally different technologies, the terms are often used today for one and the same end product: "The combination of power and data transmission in one solution". Various solutions on the market can be used as an example here. This technology is currently undergoing significant development. Whether fibre optic-based or copper, hybrid systems are increasingly conquering the industrial environment. In the past, specific applications or niches were a field of application for such technologies, but the advantages and the issue of sustainability are bringing about a change in established areas. One key to the breakthrough is the broad acceptance of Ethernet as a basis for communication. Standardised communication facilitates implementation and opens up new applications and markets. Extensive innovations are in the pipeline, particularly in the area of widely established metric circular connectors, which are widely represented on the market. The M12-M40 ranges are particularly noteworthy here.
These innovations are in line with technological topics such as Single Pair Ethernet as well as further developments to the M12 Y code. The first customer implementations and user organisations are already waiting for the launch of these new technologies. The article covers both the technical aspects of the new connector technology, the current standardisation driven by TE as well as the application benefits and the genesis through customer requirements.
Nickel phosphorus: A challenge for X-ray fluorescence measurement technology. Or is it?

Helmut Fischer GmbH Institut für Elektronik und Messtechnik
Description:
Nickel phosphorus (NiP) is known as a hard, non-magnetic and corrosion-resistant diffusion barrier from PCB technology and is increasingly being used in connectors. In contrast to PCBs, however, the demands on the measurement technology for plug contacts are higher. For example, the ability to measure the phosphorus content on the smallest measuring spots is required. The phosphor fluorescence line is difficult to excite with the X-ray fluorescence measuring devices typically used for connectors and is strongly absorbed both in the air and at the detector window. X-ray tubes with a chromium anode lead to significant improvements: Measuring time and measured value scatter can be reduced. However, what is good for phosphorus determination is not necessarily advantageous for other measurement tasks. We therefore want to take a holistic view of the chromium tube and, in addition to NiP, also investigate other typical measurement tasks for connectors in comparison to tungsten tubes.
Contact springs as a mechatronic component

KERN LIEBERS GmbH & Co. KG
Description:
Springs in various forms are increasingly being used in electromechanical applications. The preferred material here is stainless steel, which, however, has relatively poor electrical conductivity. Such electrical contacts are therefore limited in their current carrying capacity. One solution according to the state of the art is to use an additional contact element. The KERN LIEBERS Group is therefore pursuing a development approach based on high-performance copper alloys as stainless steel substitutes in order to be able to use various spring elements as a direct conductive element.
Helical compression springs, wave springs and annular springs are types of springs that are used in various applications. These different types enable customised contacting solutions depending on the installation space or load spectrum. Helical compression springs are cylindrical springs that primarily work under compressive load. Wave springs are a space-optimised alternative. Ring springs, on the other hand, consist of one or more concentric rings and offer a high load capacity under axial and radial loads. Miniaturisation is also playing an increasingly important role in the development of springs. Particularly in electromechanical applications, miniaturised springs allow space-saving integration into complex systems and are becoming increasingly important in assembly and connection technology. These are key factors that contribute to increasing the efficiency of these components. They have a high level of functional integration, as they can act as a damping element and tolerance compensation in addition to making contact, for example.
Automation of an electroplating shop with JSPS - Jentner Smart Plating System

C. Jentner
Description:
JSPS is a web-based software for the automation of manual coating processes in rack and barrel electroplating, especially for contract electroplating with a large variety of workpieces. Developed over five years, the system is now patented and is being continuously developed.
Transmitting UWB (UltraWideBand) tags and stationary antennas are used for seamless product carrier tracking, creating a kind of indoor GPS. This not only enables real-time localisation, but also the automatic triggering of processes - e.g: Booking in the goods carriers, activating peripheral devices and rectifiers.
Our software checks that the process steps are being followed correctly, sends warning and fault messages to the employees via smartphone and supports or guides them digitally through the process with the help of LED strips and HMI panels.
All recorded data flows into a data lake to enable big data analyses and pattern recognition for anomalies. In addition, we provide the relevant process data in a digital production file for the customer on request.
Thunderbolt & USB-C: The Power Duo of High-Speed Connectivity

Emerson
Description:
In this talk, we take a brief look at Thunderbolt and USB-C and examine how these two technologies together contribute to the dynamics of modern high-speed interfaces. The USB-C connector has established itself as a universal and versatile connector that combines not only data transfers, but also video and power transfers in a single connector. This physical uniformity has led to widespread acceptance in the electronics industry and enabled standardisation. While USB-C is the form factor that provides the physical connection, Thunderbolt provides superior performance in the background. Thunderbolt, driven by the collaboration between Intel and Apple, utilises the USB-C connector and extends its functionality with impressive data transfer rates of up to 40 Gbps and the ability to daisy-chain multiple devices.
We examine the technical advantages of this power duo - from its high speed and versatility to its practical application in modern laptops, desktops and docking stations. A special focus is placed on the USB-C connector itself, whose suitability as a universal connection brings numerous advantages for both consumers and manufacturers. We also take a look at the future of high-speed interfaces and how Thunderbolt and USB-C will continue to drive innovation. This presentation will provide a technical overview, real-world examples and highlight the synergy effects that the interaction of Thunderbolt and USB-C enables.
Sustainable electroplating solutions: tin plating

MKS Instruments, Inc.
Description:
Tin is the ideal surface for electrical contacts if parts need to be soldered, crimped or bolted together and has thus become the contact material for connectors. The standard process to deposit Tin on copper based materials is a galvanic process mostly applied in conveyorized high speed tools or in rack and barrel tools. Many applicators are using established tin plating processes, often in use for decades.
Traditionally, Tin electrolytes comprise a whole set of specific chemical additives, some of which are now under scrutiny by European and non European government agencies for their hazardous potential like PFAS, Siloxanes and BPA. Other substances as Pyrocatechol, used to prevent Tin 4+ precipitates, are suspected to be cancerogenic and mutagenic.
We are demonstrating with this paper that it is possible to develop and apply fully sustainable Tin electrolytes and tin protection processes with ingredients that
- are fully compliant with known and anticipated regulations (known future bans)
- pose a significantly lower health risk by avoiding cancerogenic or mutagenic additives
- fullfill all the technical requirements such as low whisker propensity, appearance, surface distribution, process stability and solderability
in direct comparison to established but non sustainable electrolytes.
Poster Slam Award Ceremony and Get Together at the VCC Vogel Convention Center
We end the day with finger food, cold drinks and plenty of time to network with participants, speakers and exhibitors.
sponsored by

Tuesday, May 27, 2025 - User Congress Day 1
(Event hall "Shedhalle")
Registration of participants at the Vogel Convention Center (VCC)
Welcome to the first day of the Connector User Congress
Listen to lectures from experts on the following topics:
- Single Pair Ethernet
- Electrical interfaces
- Simulation
- New technologies

Kristin Rinortner
ELEKTRONIKPRAXIS
Keynote Speech
On the cutting edge of new ideas - innovation management in connection technology

Head of Innovation Management | Lapp Holding SE
Focus: Single Pair Ethernet
Convergence in SPE Connectivity using PROFINET as an example
The unified SPE connector – status and implications for users

PHOENIX CONTACT GmbH & Co. KG

Rosenberger Hochfrequenztechnik GmbH & Co. KG
Coffee break and exhibition
Focus: Electrical Interfaces
Laser Structuring of Stamping Grids for Media Tight Connectors for Battery Packs, Power Electronics and Cooling Systems for E-Drives

KERN LIEBERS GmbH & Co. KG
USB-C 3.1 as an intelligent power supply and charging interface

Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH & Co. KG
Everything on the PCB: Challenges and solutions for circular connectors

PHOENIX CONTACT GmbH & Co. KG
Lunch break and exhibition
SPOTLIGHT STAGE
1:10 - 1:25 pm
High speed connector manufacturing
presented by


Greg Mitchell | CEO
1:25 - 1:40 pm
5 steps to increase your competitive advantage with precision moulding tools
presented by


Ingo Böhm | Senior Sales Manager
Parallel Workshops
(VCC seminar rooms)
Workshop 1: Measurement system analysis to optimize quality controls using X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF)
Dr. Konstantinos Panos | Helmut Fischer GmbH
Omar Cheikh-Jumaa | Helmut Fischer GmbH
Focus: Checking & Testing
Workshop 2: Success in new markets through leak testing of connectors
Dr. Joachim Lapsien | CETA Testsysteme GmbH
Focus: Checking & Testing
Workshop 3: Flexible and precise manufacturing of connectors
Kay Wesendrup | Otto Bihler Maschinenfabrik GmbH & Co. KG
Christian Franke | Otto Bihler Maschinenfabrik GmbH & Co. KG
Focus: Manufacturing
Short coffee break and exhibition
Focus: Simulation
EMC and the simulation that nobody actually wants to do

Simuserv GmbH
Coffee break and exhibition
Focus: New Technologies
Latest technologies in the metal recycling economy of the connector industry

Silverteam Recycling GmbH
On the brink of the future: How the connector industry shapes the AI revolution

Heilind Electronics GmbH
Summary and information about the evening event

Kristin Rinortner
ELEKTRONIKPRAXIS
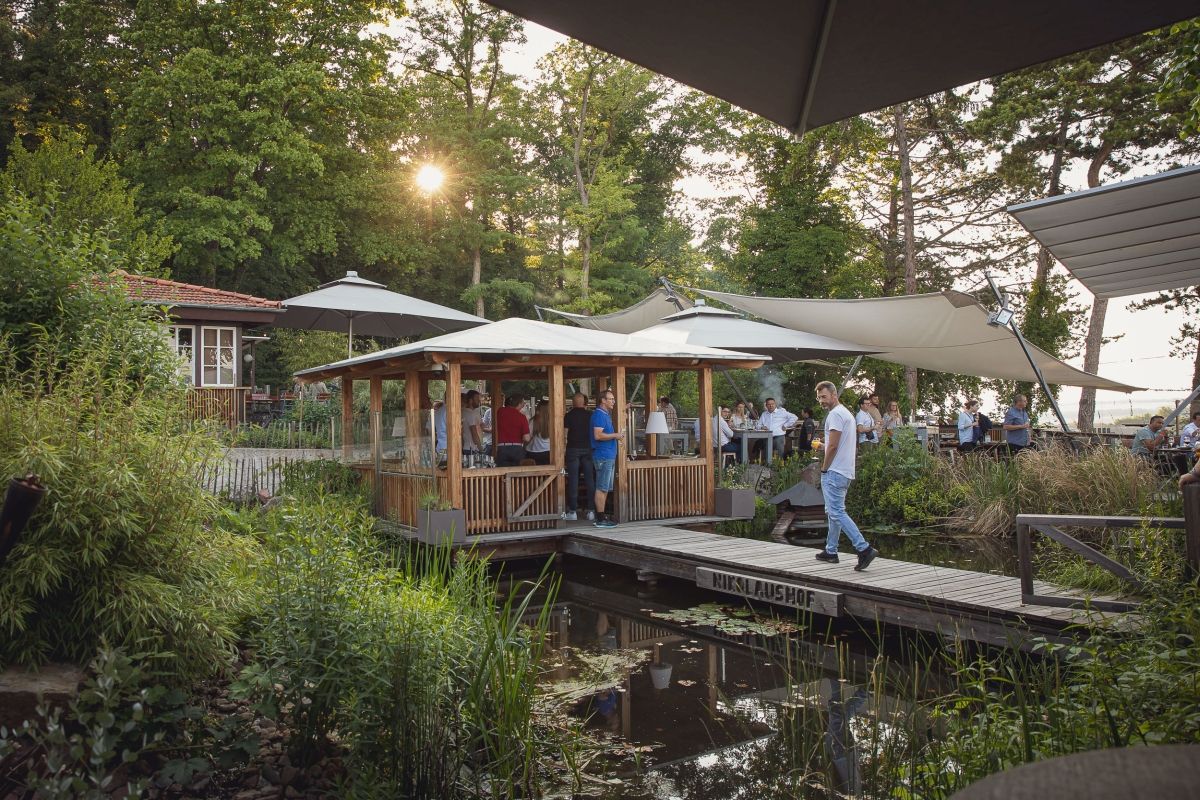
Evening event at the Nikolaushof Würzburg
Wednesday, May 28, 2025 - User Congress Day 2
(Event hall "Shedhalle")
Registration of participants at the Vogel Convention Center
Welcome to the second day of the Connector User Congress
Listen to lectures from experts on the following topics:
- Automotive
- Materials and coatings

Kristin Rinortner
ELEKTRONIKPRAXIS
Focus: Automotive
Reliability engineering for automotive connectors – Risks and opportunities at the same time

TE Connectivity Germany
Ultrasonic welding of Al busbars to Cu contacts: The role of laser structuring and connection reliability in meeting IEC 60352-9 standards

Schaltbau GmbH
Forming limits and maximum formabilities of metallic materials for connectors in the automotive industry

TE Connectivity Germany
Coffee break and exhibition
Focus: Materials and Coatings
Sustainable production of circular connectors: Potential of metal forming for ecological and economic benefits

Manufacturing Technology Institute - MTI der RWTH Aachen

Eichsfelder Schraubenwerk GmbH
Metals and clad materials for electrical connectors in high performance applications

Materion Brush GmbH
Aging of plastics in terms of dielectric strength and tracking resistance

Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH & Co. KG
Summary and Outlook 2026

Kristin Rinortner
ELEKTRONIKPRAXIS
Lunch break and exhibition
SPOTLIGHT STAGE
1:20 - 1:35 pm
What VAD really means
presented by


Oliver Fleschhut | European Mil/Aero Product Team Leader
Parallel Workshops
(VCC seminar rooms)
Workshop 1: Measurement system analysis to optimize quality controls using X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF)
Dr. Konstantinos Panos | Helmut Fischer GmbH
Omar Cheikh-Jumaa | Helmut Fischer GmbH
Focus: Checking & Testing
Workshop 2: Success in new markets through leak testing of connectors
Dr. Joachim Lapsien | CETA Testsysteme GmbH
Focus: Checking & Testing
Workshop 3: Flexible and precise manufacturing of connectors
Kay Wesendrup | Otto Bihler Maschinenfabrik GmbH & Co. KG
Christian Franke
| Otto Bihler Maschinenfabrik GmbH & Co. KG
Focus: Manufacturing
End of the Connector User Congress 2025
* Subject to change
** Our service for participants in the basic seminars: You will receive the Practical Manual for Connectors worth €89.80.